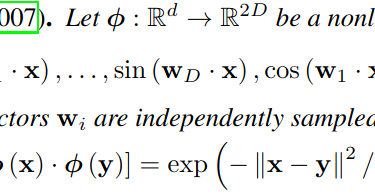Machine Translation Weekly 77: Reference-free Evaluation
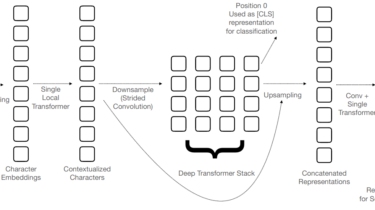
This week, I am will comment on a paper by authors from the University of Maryland and Google Research on reference-free evaluation of machine translation, which seems quite disturbing to me and suggests there is a lot about current MT models we still don’t quite understand. The title of the paper is “Assessing Reference-Free Peer Evaluation for Machine Translation” and it will be published at this year’s NAACL conference. The standard evaluation of machine translation uses reference translations: translations that […]
Read more