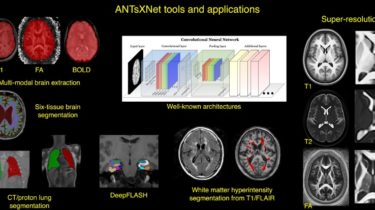
Docker can slow down your code and distort your benchmarks
One of the benefits of containers over virtual machines is that you get some measure of isolation without the performance overhead or distortion of virtualization. Docker images therefore seem like a good way to get a reproducible environment for measuring CPU performance of your code. There are, however, complications. Sometimes, running under Docker can actually slow down your code and distort your performance measurements. On macOS and Windows, for example, standard Linux-based Docker containers aren’t actually running directly on the […]
Read more