Challenges In Automated Review Analysis
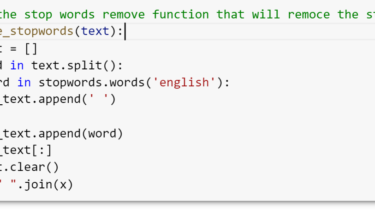
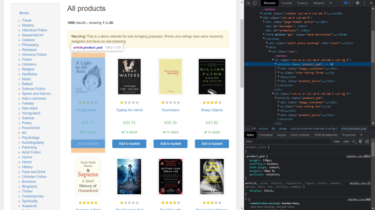
Determining sentiment in the text using neural network models has become almost a school task for beginner data scientists. However, despite the high quality of models and the ease of working with them, it is not so easy to characterize real data from reviews of restaurants, hotels, or museums. Even Google’s algorithms can’t do it properly. What are
Read more