Selectively Precoded Polar Codes
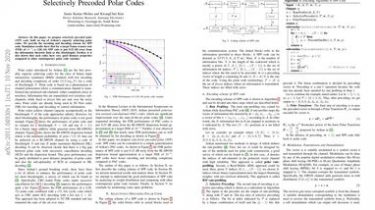
In this paper, we propose textit{selectively precoded polar (SPP) code}, built on top of Arikan’s capacity achieving polar codes. We provide the encoding and decoding scheme for SPP code… Simulation results show that for a target frame erasure rate (FER) of $10^{-5}$, a (128, 64) SPP code is just 0.23 dB away from the information theoretic limit at this blocklength. Further, it is also shown that such codes have very good distance properties compared to other contemporary polar code variants. […]
Read more